Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Technical Terms
Centralized Finance (CeFi)
Centralized finance, often abbreviated as CeFi, refers to traditional financial systems and institutions that operate in a centralized manner. In CeFi, intermediaries such as banks, financial institutions, and other centralized entities play a significant role in facilitating financial transactions, managing funds, and providing financial services.
Here are some key characteristics of centralized finance:
1. Centralized Control: In CeFi, a central authority or institution exercises control over the financial system. This central entity manages customer accounts, controls access to funds, and oversees the operation of the financial services.
2. Trusted Intermediaries: CeFi relies on trusted intermediaries, such as banks or financial institutions, to facilitate transactions and manage user funds. These intermediaries act as custodians, holding and safeguarding customer assets on their behalf.
3. Regulatory Compliance: CeFi institutions are subject to various regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements imposed by governments and financial authorities. These regulations aim to ensure transparency, consumer protection, and mitigate risks within the financial system.
4. Limited Accessibility: CeFi services are typically limited to individuals and entities that meet specific criteria set by the centralized institution. This may include requirements such as minimum balance thresholds, creditworthiness assessments, or geographic restrictions.
5. Traditional Banking Infrastructure: CeFi institutions utilize traditional banking infrastructure, including physical branches, legacy payment systems, and traditional record-keeping methods.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a word that well-known in the world of cryptocurrency. DeFi is a word you must know if you are a beginner and you want to research cryptocurrency. Let’s talk about DeFi and How it’s different from a bank.
DeFi is a financial tool that uses the concept of decentralization. In traditional finance, we are familiar with bank which is centralized. So if you want to send some transactions, you need permission from the center. In DeFi, the important thing is the idea of decentralization which makes DeFi different from traditional finance.
Decentralized system powered by the technology blockchain and the automated program that runs on blockchain called smart contracts. This gives the user a lot of opportunities, for example, the lending system that anyone can be a lender or borrower without permission from the center.
DeFi has a lot of types, for example, decentralized exchange, derivatives, yield farming, launchpad, etc. Of course, all of them are decentralized and use the idea of a trustless system.
Blockchain
What makes cryptocurrency so special? Is it good? Can we trust them and what runs crypto's mechanism? We'll explain what's the technology behind cryptocurrency. It's a technology called Blockchain.
Instead of centralized database or server that we familiar with, Blockchain is a technology that allows device across the network to be distributed database or ledger. It stores information entirely in digital format.
The way that blockchain stores data is the key difference between traditional database. When fresh and new data came into the network, it will create a new block, then a mechanism called 'Consensus Model' (PoW and PoS) will create a key that linked back to previous block like a chain.
After the block create hash and already chained into the network, that data will never be able to modify, delete, or destroy. Those data will transparency and allow anybody to track and validate the correctness. Also, it's decentralized, no single person or group has control.
That's why we can trust blockchain, so, cryptocurrency is one of the use cases of blockchain. When you execute the transaction, blockchain and their nodes help to approve and store that transaction into the network instead of traditional banker that must approve your transaction.
Proof of Work (PoW)
When BitCoin went viral in 2017-18, many people may have known that graphic card (GPU) started to shortage, its price is very high because most of the buyers bought it to build a BitCoin mining machine.
Proof of Work (PoW) that used in BitCoin network is the reason why we need high efficiency of computational machine to mine it. In order to create a new block, each node will racing to solve a Hash puzzle to be the first for create a hash key that linked back to previous block.
The winning miner who can solve that hash will receive a reward, that's why many people start invest to build a giant mine.
However, the cost is very high and it’s consume a lot of electricity, so, it's difficult to break the even point and also caused a climate change.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
The main purpose of Proof of Stake (PoS) is still the same as PoW which is trying to validate a new block and create hash key that linked with the previous block. But the process to get the hash key is the key difference from PoW.
The word 'Stake' in PoS is quite consistent with its meaning. It means you have to stake coin into a system to become a 'Validator' and you'll have chance to validate a new block for the network. But why did we say 'will have a chance'?
Because the validator will be chosen randomly, so, every validators will have an equal chance to validate the new block and create a hash key, instead of being the first one to create a hash key like PoW.
To be clear, stake coins into a system is like when you deposit your money with the bank and receive an interest per year. But in DeFi world, we called this staking and get reward in form of APR (Annual Percentage Rate) as a percentage.
This mechanism also affected to transaction fees or Gas fees which make users who want to execute the transaction, pay significantly less gas fees. Because there's no need to use a lot of resources like PoW.
From all those advantages of PoS, Etheruem chain has already moved from PoW to PoS! So, gas fees on Ethereum is significantly dropped than before. To become a validator on Ethereum chain, you must staked 32ETH or staked using 'Liquid Staking' as an alternative way.
Smart Contract
In traditional bank, when you wants to transfer your money or any payment transaction, bank needs to be a middle-man to verify the transaction. But it is difference in Decentralized Finance that uses Smart Contract.
Smart Contract was first developed by Vitalik Buterin, the Ethereum founder. That means the first use of Smart Contract is on Ethereum chain that launched in 2014. This is the feature that unlock the capabilities of using cryptocurrency and making transaction.
To be simply, Smart Contract a set of programming code that use to verify the transaction. That means we use computer to verify transaction for us, so, we can guarantee that the transaction will execute only if conditions are matched with smart contract.
More than that, every smart contracts were deployed on Blockchain which makes the code exposed, everyone can see the code in smart contract. It sounds good when someone said,
"We can knows that this is a fraud contract or cheated by seeing all codes".
However, it's not everyone can read and understand the code. So, exposed code is not actually an advantage. Even we understand all codes, it doesn't mean there is no way a leaked hole for cheating.
Gas
To successfully execute the transaction, we need to pay Gas fee. Since it was a small fraction of ETH, so, it has another unit specially for gas fee called gwei (equal ETH). The exact gas price is depends on demand, supply, and network capacity.
Gas fee is calculated from 2 value, Gas Limit and Gas Price. Gas limit is the maximum amount of work that you need to estimating. A higher gas limit is means the transaction will require more work. Gas Price is the price per unit of work done, usually depends on the network.
Therefore, . For example, you put a gas limit of 50,000 gwei and after calculated, it turns out that Gas Fee is only 21,000 gwei, so, you'll get 29,000 gwei back as refund.
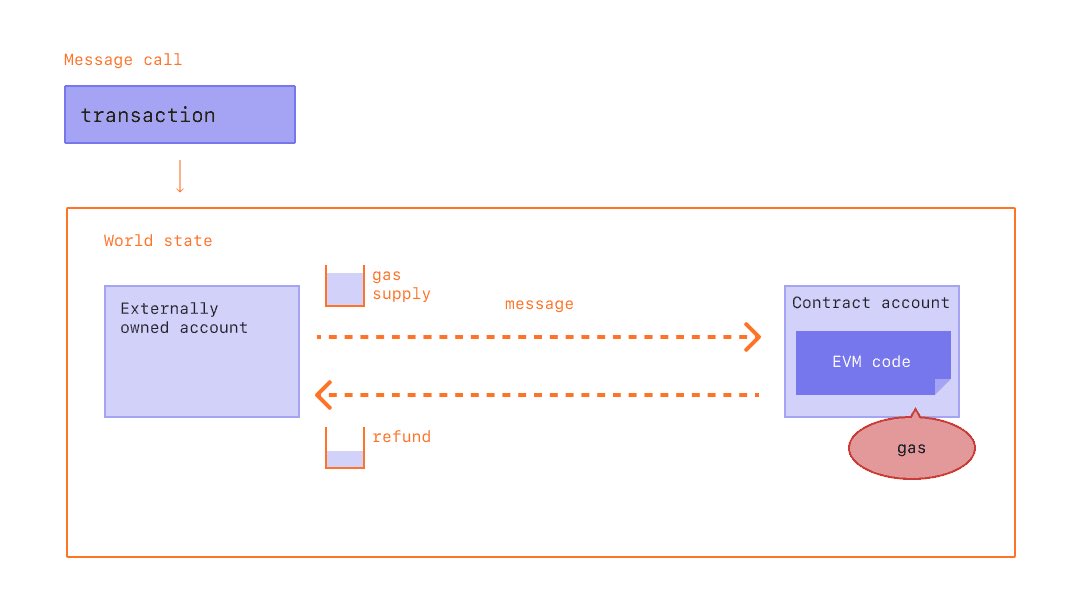
However, if you entered Gas Limit too low, the transaction won't complete and you'll lost the gas limit that you had input.
Blocktime
In Ethereum, block time refers to the time it takes to mine or generate a new block on the Ethereum blockchain. It represents the interval between the mining of two consecutive blocks. Ethereum, like many other blockchain networks, uses a consensus algorithm called Proof of Work (PoW) to validate and add new blocks to the blockchain.
In Ethereum's PoW algorithm, miners compete to solve a complex mathematical problem by expending computational power. The miner who successfully solves the problem first gets the opportunity to add the next block to the blockchain and receives a reward in the form of Ether (ETH). The block time is the average time it takes for miners to find a valid solution and mine a new block.
In the past, the average block time for Ethereum was around 15 seconds. However, the Ethereum network has undergone several upgrades, including the implementation of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which introduced a transition from PoW to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This transition aims to improve scalability, security, and energy efficiency.
As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, Ethereum 2.0 is still being rolled out, and the PoS mechanism is being phased in. The block time in the upgraded Ethereum network is expected to be around 12 seconds initially, but it may vary based on network conditions and future upgrades. It's important to note that the actual block time can fluctuate due to factors such as network congestion, mining difficulty, and the number of active participants in the network.
Initial Coin Offering (ICO)
An Initial Coin Offering (ICO) is a method for raise money to create new project that related to crypto industry. People who fundraise in ICO will get reward as "Token" or "Coin", this token is related in project's ICO, for example, this token is a cryptocurrency in that project.
In other words, ICO is a method that company sell "Idea" in term of "Token". Investors who interested or want to invest in this idea can buy these tokens. Revenue from sales will be used to develop project to make it happen.
ICO have a various methods, in this section, we want to explained a four methods that easy to understand.
1. Capped First-Come First-Served: A company set specific funding goal and fixed price per token.
2. Uncapped: A company fixed price per token but dynamic funding goal.
3. Capped with re-distribution: A company fixed number of tokens are sold at a fixed price. Then allow investors to invest money they want to buy, after ICO ended, investor will receive token(s) depend on proportion of each investor's total spend.
4. Capped with parcel limit: Same as Capped First-Come First-Served method, but limit amount of tokens that investor able to buy.
Initital DEX Offering (IDO)
IDO or Initial DEX Offering is a crowdfunding technique that allows cryptocurrency projects to lunch their native token through Decentralized Exchange (DEX). (If you don't know about DEX, we recommend you read it first in this thread)
The main difference between ICO and IDO is: ICO is raising funds for a cryptocurrency on the project owner’s website, but IDO raises funds via DEX that Decentralized and provides investors with a higher level of security.
What makes an IDO unique is anyone does not require large sums of money to participate. Also, no identification requirement makes investors insecure. In security, IDO uses Smart contract for each transaction. These smart contracts are provided only by DEX. These platform doesn't keep track of the user's Private key, or private information.
Market Capitalization (Market Cap.)
In the context of cryptocurrencies, market capitalization (market cap) is a metric used to assess the size and value of a specific cryptocurrency. It provides an estimate of the total value of a cryptocurrency in the market.
To calculate the market capitalization of a cryptocurrency, you multiply the current price of a single token by the total supply of tokens in circulation. This calculation gives you the total value of all the tokens available for that cryptocurrency.
For example, let's say a cryptocurrency has a current price of $10 per token, and there are 10 million tokens in circulation. The market capitalization would be calculated as:
Market Cap = Current Price per Token * Total Supply of Tokens
Market Cap = $10*10,000,000 = $100,000,000
In this case, the market capitalization of the cryptocurrency would be $100 million.
Market capitalization is used to compare different cryptocurrencies and rank them based on their relative size or value within the cryptocurrency market. Cryptocurrencies with higher market capitalizations are generally considered to be larger and more valuable.
Based on market capitalization, cryptocurrencies are often categorized into different tiers, such as large-cap, mid-cap, or small-cap. These categories indicate the size and relative value of the cryptocurrency within the overall market.
It's important to note that market capitalization can change dynamically as the price of the cryptocurrency fluctuates and as new tokens are issued or burned. Market capitalization is just one measure used to assess the value and size of a cryptocurrency, and it should be considered alongside other factors such as trading volume, community support, development activity, and the underlying technology when evaluating or investing in cryptocurrencies.
Fully Diluted Market Capitalization (FDMC)
The fully diluted market cap is the total value of the crypto at today’s price if all tokens are in circulation. By using this capitalization method, it is assumed that the market cap in the future will grow in line with the amount of circulating supply at a given moment.
In some cases, an increase in token supply can occur, leading to market inflation with the oversupply. As a result, the token prices can be dropped. Therefore, many crypto investors are afraid of increasing the supply of coins or tokens in circulation.
Total Value Lock (TVL)
To understand TVL, let we explain a simple example. This system called "Bank". We deposit our money to the bank, that make bank to have money from depositors to circulate in the system. This is the same process in DeFi world, we deposit cryptocurrency to DeFi platform, our cryptocurrency that circulating in the system is called "TVL". (TVL stand for "Total Value Locked")
The TVL indicator is more helpful, because DeFi platform which have higher TVL means investors around the world trust these platforms have the potential to grow in the future. (TVL is one of the DeFi indicators, there are a lot of factors that used to indicate DeFi projects.)
Total Supply
Total Supply refers to the total amount of coins or tokens of a specific cryptocurrency that have been created or mined, that are in circulation, including those that are locked or reserved.
Total Volume
Trading volume in crypto refers to the total amount of a digital asset traded over a certain period. This metric indicates the trading activity of a coin in the entire market or on an exchange. Typically, exchanges measure trading volume for the past 24 hours.
On-Chain Data
Daily Active User
In the context of blockchain, daily active users refer to the number of unique addresses or wallets that are actively involved in transactions on a specific blockchain network within a 24-hour period. Each user may have multiple transactions or interactions within that timeframe, but they are counted as a single active user.
Tracking daily active users on a blockchain can provide insights into the adoption and usage of a particular blockchain network or decentralized application (dApp). It can help gauge the popularity and engagement levels of the network, measure user activity, and assess the overall health of the ecosystem.
The number of daily active users can vary significantly depending on the blockchain platform, its use cases, and the applications built on top of it. Some popular blockchains like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Solana have thousands or even millions of daily active users, while smaller or niche blockchains may have fewer active users.
It's worth noting that tracking daily active users on a blockchain can be more challenging compared to traditional centralized applications, as blockchain transactions are typically pseudonymous and not directly tied to individual identities.
Allocation
In the context of cryptocurrency, "allocation" typically refers to the distribution or assignment of funds or resources to specific purposes or entities within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. It involves dividing or allocating tokens, coins, or assets among different participants or stakeholders for various reasons.
Here are a few common types of allocations in the cryptocurrency space:
1. Token Allocation: During the initial launch of a cryptocurrency project or initial coin offering (ICO), tokens are allocated or distributed to investors, contributors, and team members. These allocations may be used to raise funds, incentivize participation, or reward early supporters.
2. Token Sale Allocation: When a cryptocurrency project conducts a public token sale, a certain percentage of tokens are allocated for sale to the general public. These allocations are usually sold at predetermined prices or through various sale mechanisms such as auctions, token sales, or token swaps.
3. Community Allocation: Some cryptocurrency projects allocate a portion of their tokens to community members, often through a process called airdrops. These allocations are distributed to individuals who meet specific criteria, such as holding a certain amount of a particular token, actively participating in the project's community, or completing certain tasks.
4. Development and Team Allocation: Cryptocurrency projects may allocate tokens or funds to support the development of the project, cover operational expenses, or compensate team members and advisors. These allocations ensure that the project has the necessary resources to grow and achieve its goals.
5. Liquidity Pool Allocation: In decentralized finance (DeFi), liquidity pools are created by users who contribute their cryptocurrency assets to a pool in exchange for earning rewards. These allocations of liquidity provide the necessary liquidity for decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, or other DeFi protocols to function effectively.
It's important to note that allocation strategies and distribution mechanisms can vary widely among different cryptocurrency projects. The purpose of these allocations can range from fundraising, incentivizing participation, building community support, or fostering liquidity in the ecosystem. Each project may have its own unique allocation plan based on its goals, governance structure, and token economics.
Fee and Revenue
Most of the product in DeFi make profit by collecting fees from each transaction that have been made on their platform.